This content is authored by Red Hat experts, but has not yet been tested on every supported configuration.
Deploy the OpenShift Virtualization Operator
Deploy the OpenShift Virtualization Operator
cat << EOF | oc apply -f - apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: openshift-cnv --- apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1 kind: OperatorGroup metadata: name: kubevirt-hyperconverged-group namespace: openshift-cnv spec: targetNamespaces: - openshift-cnv --- apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1 kind: Subscription metadata: name: hco-operatorhub namespace: openshift-cnv spec: source: redhat-operators sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace name: kubevirt-hyperconverged startingCSV: kubevirt-hyperconverged-operator.v4.15.1 channel: "stable" EOFIf you want to see the progress of the operator you can log into the OpenShift Console (hint run
oc whoami --show-consoleto get the URL)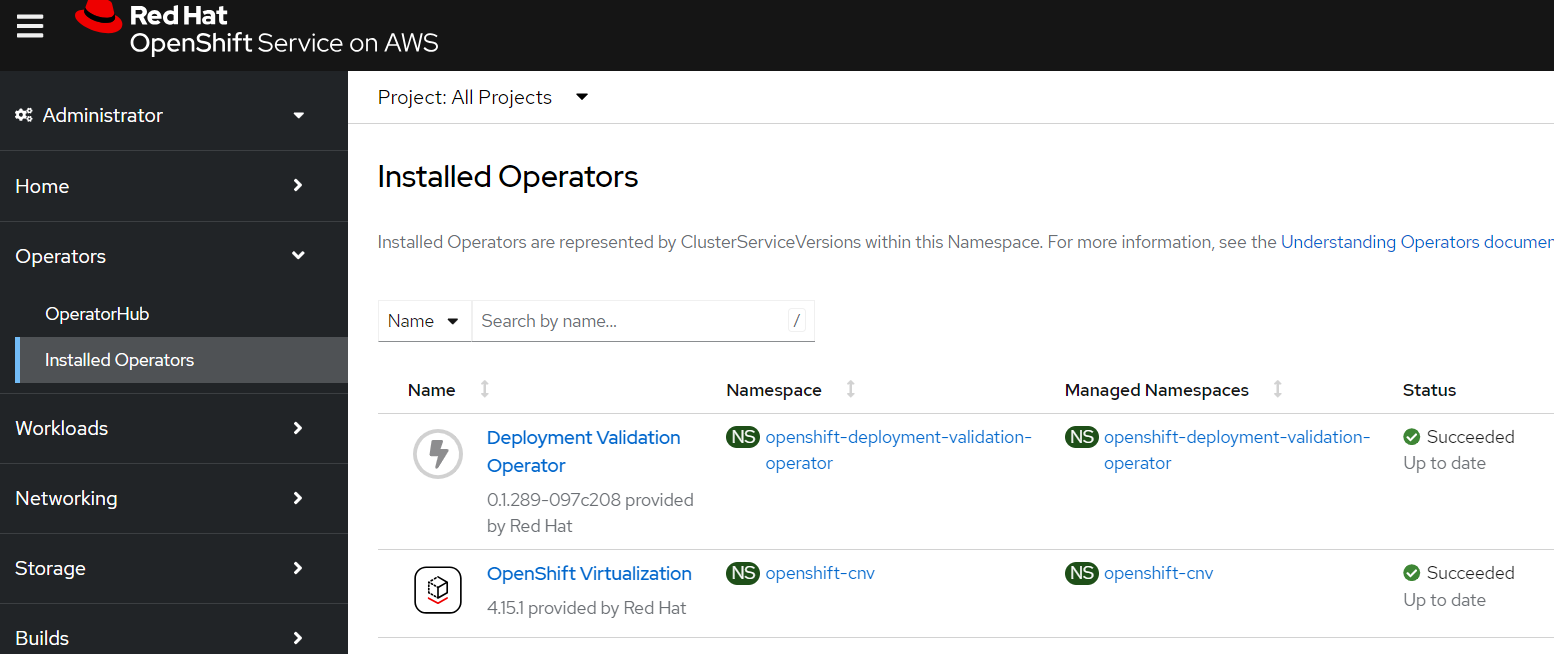
Create an OpenShift Virtualization operand
Note: this is all defaults, so will not support a lot of the more advanced features you might want such as live migration.
cat << EOF | oc apply -f - apiVersion: hco.kubevirt.io/v1beta1 kind: HyperConverged metadata: annotations: deployOVS: "false" finalizers: - kubevirt.io/hyperconverged generation: 2 labels: app: kubevirt-hyperconverged name: kubevirt-hyperconverged namespace: openshift-cnv spec: applicationAwareConfig: allowApplicationAwareClusterResourceQuota: false vmiCalcConfigName: DedicatedVirtualResources certConfig: ca: duration: 48h0m0s renewBefore: 24h0m0s server: duration: 24h0m0s renewBefore: 12h0m0s evictionStrategy: LiveMigrate featureGates: alignCPUs: false autoResourceLimits: false deployKubeSecondaryDNS: false deployTektonTaskResources: false deployVmConsoleProxy: false disableMDevConfiguration: false enableApplicationAwareQuota: false enableCommonBootImageImport: true enableManagedTenantQuota: false nonRoot: true persistentReservation: false withHostPassthroughCPU: false infra: {} liveMigrationConfig: allowAutoConverge: false allowPostCopy: false completionTimeoutPerGiB: 800 parallelMigrationsPerCluster: 5 parallelOutboundMigrationsPerNode: 2 progressTimeout: 150 resourceRequirements: vmiCPUAllocationRatio: 10 uninstallStrategy: BlockUninstallIfWorkloadsExist virtualMachineOptions: disableFreePageReporting: false disableSerialConsoleLog: true workloadUpdateStrategy: batchEvictionInterval: 1m0s batchEvictionSize: 10 workloadUpdateMethods: - LiveMigrate workloads: {} EOFNew “Virtualization” Section in the OpenShift Console
Once the operator is installed you should see a new “Virtualization” section in the OpenShift Console (you may be prompted to refresh the page)
Close the popup window and click the “Download virtctl” button to download the
virtctlbinary.
